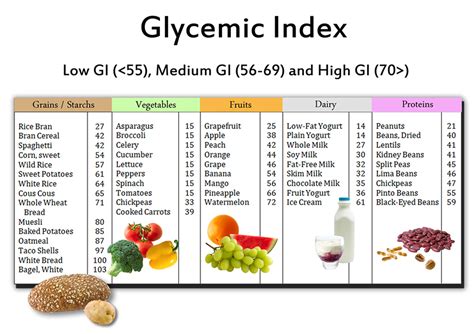
givenchy index and type two diabetes | niddm low glycemic index givenchy index and type two diabetes In this short review, we examine evidence relating dietary glycemic index and glycemic load to type 2 diabetes incidence and the role of the form of dietary carbohydrate in the management of diabetes. Jugendrotkreuz Brandenburg - Wir halten als Team immer zusammen! 57 views2 years ago. Willkommen auf dem offiziellen Youtube-Kanal des DRK-Landesverband Brandenburg e.V.Das DRK im.
0 · what is the glycemic index
1 · niddm low glycemic index
2 · low glycemic index for diabetics
3 · high glycemic index type 2 diabetes
4 · high glycemic index and diabetes
5 · glycemic load diabetes type 2
LOUIS VUITTON Official UAE site - Explore the World of Louis Vuitton, read our latest News, discover our Women and Men Collections and locate our Stores.
what is the glycemic index
In this short review, we examine evidence relating dietary glycemic index and glycemic load to type 2 diabetes incidence and the role of the form of dietary carbohydrate in the management of diabetes.Statistical interaction for GI indicated a high RR for smaller cohort size for type 2 diabetes and total cardiovascular disease, whereas a larger cohort size for all-cause mortality. A high RR .
how long is the michael kors sale going on
In this short review, we examine evidence relating dietary glycemic index and glycemic load to type 2 diabetes incidence and the role of the form of dietary carbohydrate in the management of diabetes.Statistical interaction for GI indicated a high RR for smaller cohort size for type 2 diabetes and total cardiovascular disease, whereas a larger cohort size for all-cause mortality. A high RR was also observed for a shorter follow-up duration for type 2 diabetes, but a longer duration for total cardiovascular disease.We aimed to assess the associations between glycaemic index (GI) and glycaemic load (GL) and type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, diabetes-related cancers, and all-cause mortality. Methods: We did a meta-analysis of large cohorts (≥100 000 participants) identified from the Richard Doll Consortium.
Glycemic index and glycemic load are dietary factors probably causal of type 2 diabetes and should be considered by future dietary guideline committees for inclusion in food and nutrient-based recommendations.The current analyses include data from an outlier showing far higher association between glycaemic index and type 2 diabetes than other studies, easily detected with influence analysis, further challenging the concept that the chosen cohorts provide consistent results.
Published meta-analyses indicate significant but inconsistent incident type-2 diabetes (T2D)-dietary glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) risk ratios or risk relations (RR). It is now over a decade ago that a published meta-analysis used a predefined standard to identify valid studies. The ADA, WHO, and IHS guidelines recommend that adults be evaluated for type 2 diabetes if they are overweight (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m 2) and have one or more of the following risk factors: first-degree relative with diabetes, women who delivered a baby weighing > 9 lb, diagnosis of hypertension > 140/90 mmHg, diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome .Background: The association between the glycaemic index and the glycaemic load with type 2 diabetes incidence is controversial. We aimed to evaluate this association in an international cohort with diverse glycaemic index and glycaemic load diets.
Metabolic surgery is a recommended treatment option for adults with type 2 diabetes and 1) a BMI ≥40.0 kg/m 2 (BMI ≥37.5 kg/m 2 in people of Asian ancestry) or 2) a BMI of 35.0–39.9 kg/m 2 (32.5–37.4 kg/m 2 in people of Asian ancestry) who do not achieve durable weight loss and improvement in comorbidities with reasonable nonsurgical .Research has shown that choosing low-GI foods can particularly help manage long-term blood glucose (HbA1c) levels in people with type 2 diabetes. There is less evidence to support this in people with type 1 diabetes, but we know that on a day-to-day basis choosing low GI foods can help keep blood glucose levels steady after eating.In this short review, we examine evidence relating dietary glycemic index and glycemic load to type 2 diabetes incidence and the role of the form of dietary carbohydrate in the management of diabetes.Statistical interaction for GI indicated a high RR for smaller cohort size for type 2 diabetes and total cardiovascular disease, whereas a larger cohort size for all-cause mortality. A high RR was also observed for a shorter follow-up duration for type 2 diabetes, but a longer duration for total cardiovascular disease.
We aimed to assess the associations between glycaemic index (GI) and glycaemic load (GL) and type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, diabetes-related cancers, and all-cause mortality. Methods: We did a meta-analysis of large cohorts (≥100 000 participants) identified from the Richard Doll Consortium.Glycemic index and glycemic load are dietary factors probably causal of type 2 diabetes and should be considered by future dietary guideline committees for inclusion in food and nutrient-based recommendations.The current analyses include data from an outlier showing far higher association between glycaemic index and type 2 diabetes than other studies, easily detected with influence analysis, further challenging the concept that the chosen cohorts provide consistent results. Published meta-analyses indicate significant but inconsistent incident type-2 diabetes (T2D)-dietary glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) risk ratios or risk relations (RR). It is now over a decade ago that a published meta-analysis used a predefined standard to identify valid studies.
The ADA, WHO, and IHS guidelines recommend that adults be evaluated for type 2 diabetes if they are overweight (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m 2) and have one or more of the following risk factors: first-degree relative with diabetes, women who delivered a baby weighing > 9 lb, diagnosis of hypertension > 140/90 mmHg, diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome .Background: The association between the glycaemic index and the glycaemic load with type 2 diabetes incidence is controversial. We aimed to evaluate this association in an international cohort with diverse glycaemic index and glycaemic load diets.Metabolic surgery is a recommended treatment option for adults with type 2 diabetes and 1) a BMI ≥40.0 kg/m 2 (BMI ≥37.5 kg/m 2 in people of Asian ancestry) or 2) a BMI of 35.0–39.9 kg/m 2 (32.5–37.4 kg/m 2 in people of Asian ancestry) who do not achieve durable weight loss and improvement in comorbidities with reasonable nonsurgical .
niddm low glycemic index
low glycemic index for diabetics
is michael kors still shipping
high glycemic index type 2 diabetes

acabe com cabo e utilize seu computador desktop com wifi, ou em seu notebook com o wifi danificado, smart tv, entre outros aparelhos!!!DriverBooster: http.
givenchy index and type two diabetes|niddm low glycemic index